2 Nov 2022
Drug Trends output:
Trends in drug-related hospitalisations in New South Wales, 1999-2021
Trends in drug-related hospitalisations in New South Wales, 1999-2021
.cropimg.width=335.crop=video.png)
Key findings
This summary report presents findings on all drug-induced deaths (i.e., overdose and other drug-induced deaths where drugs have been deemed the underlying cause of death) in New South Wales from 1999-00 to 2020-2021.
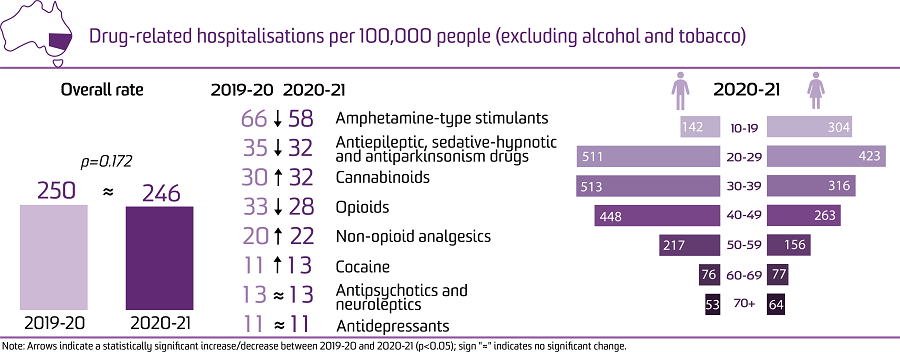
There were 18,957 hospitalisations with a drug-related principal diagnosis in New South Wales in 2020-21, equivalent to 0.57% of all hospitalisations in the state.
This is equivalent to 246 hospitalisations per 100,000 people, which is similar to the rate in 2019-20 (250 hospitalisations per 100,000 people; p=0.172), but an increase from 223 hospitalisations per 100,000 people in 1999-00.
These findings are part of the national report Trends in drug-related hospitalisations in Australia, 1999-2021.
Our public online data visualisation allows viewers to disaggregate data in different ways, and to download these images for their own use.
Chrzanowska, A., Man, N., Akhurst, J., Sutherland, R., Degenhardt, L. & Peacock, A. (2022). Trends in drug-related hospitalisations in Australia, 1999-2021. Sydney: National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, UNSW Sydney. DOI: 10.26190/wrsv-3b78
We acknowledge the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare and jurisdictional data custodians for the provision of data from the National Hospital Morbidity Database.
The Drug Trends program is funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care under the Drug and Alcohol Program.
Please note that any representation of these data should include an acknowledgment of Drug Trends at the National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, University of New South Wales.
©NDARC, UNSW SYDNEY 2022
This work is copyright. You may download, display, print and reproduce this material in unaltered form only (retaining this notice) for your personal, non-commercial use or use within your organisation. All other rights are reserved. Requests and enquiries concerning reproduction and rights should be addressed to the information manager, NDARC, UNSW Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia via drugtrends@unsw.edu.au.
2 Nov 2022
National Illicit Drug Indicators Project (NIDIP) reports
Download this resource
Contact
Research areas
In 2020-21, the rate of hospitalisations was higher among males than females (273 versus 220 hospitalisations per 100,000 people, respectively).
In 2020-21, the rate of hospitalisations was highest among the 20-29 age group, followed by the 30-39 and 40-49 age groups (469, 414, and 355 hospitalisations per 100,000 people, respectively). Among males, the rate of drug-related hospitalisations was highest in the 30-39 and 20-29 age groups, and among females in the 20-29 age group.
The highest rate of hospitalisations in 2020-21 was observed in remote and very remote New South Wales (81 hospitalisations, 279 per 100,000 people), while the number of hospitalisations was highest in major city areas (14,945 hospitalisations, 250 per 100,000 people).
In 2020-21, 34% of drug-related hospitalisations in New South Wales were due to drug poisoning. Furthermore, 69% of drug poisoning related hospitalisations were intentional (59 hospitalisations per 100,000 people) and 23% were unintentional (18 hospitalisations per 100,000 people).
In 2020-21, the rate of hospitalisations was highest where there was a principal diagnosis indicating amphetamine-type stimulants (58 hospitalisations per 100,000 people).
Compared to 2019-20, there were significant decreases in 2020-21 in the rates of hospitalisations related to amphetamine-type stimulants; antiepileptic, sedative-hypnotic and antiparkinsonism drugs; and opioids (p<0.050).
In contrast, there were significant increases in the rates of hospitalisations related to multiple drug use; cannabinoids; non-opioid analgesics; and cocaine (p<0.050).
Age-standardised rate per 100,000 people of drug-related hospitalisations, by sex, New South Wales, 1999-00 to 2020-21.
Age-standardised rate per 100,000 people of drug-related hospitalisations, by remoteness, New South Wales, 2012-13 to 2020-21.
Note: The size (area) of the bubble is proportional to the number of hospitalisations. Data on remoteness are only available from 2012-13.
Age-standardised rate per 100,000 people of drug-related hospitalisations, by principal diagnosis of mental and behavioural disorder due to substance use (A) and external cause of poisoning (B), New South Wales, 1999-00 to 2020-21.
Age-standardised rate per 100,000 people of drug-related hospitalisations, by drug identified in the principal diagnosis, New South Wales, 1999-00 to 2020-21.
Note: Age-standardised rates were not calculated if the number of hospitalisations was less than or equal to 10 (please refer to our methods document for details). Suppressed data are visible as gaps in the data series.