Archived
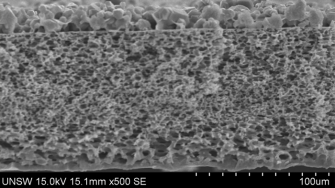
Polymer inclusion membranes (PIM), when compared to supported liquid membrane (SLM) exhibit excellent stability while retaining most of the advantages of SLMs. The current study on PIM focuses on flat-sheet membranes, however, by contrast hollow-fiber membranes possesses other advantages, such as high packing density, high surface area and low transport resistance. In this project, a preparation method using dip-coating technique for PIM was developed and evaluated. The coated membrane fibers were evaluated for their microscopic structure by SEM and separation performance through mass transport experiments of cadmium.
Factors influencing the mass transport in the extraction tests including the thickness of coated PIM on hollow fibers, feed flow rate, carrier concentration and choice of substrate were studied. The preliminary results indicated that coated PIM layer thickness and substrate type are crucial factors affecting the transport rate. Composite hollow fiber PIM membrane will be compared with the flat-sheet membranes and further optimization will be made.
Membrane Material Development
+61 2 9385 6092
- Research team
- Collaborators
Xiong Yi Farzad
Rahim Rajabzadeh
Hongyu Li
Vicki Chen
Spas Kolev
University of Melbourne
